
The only other possible pairings are GT and AC these pairings are mismatches because the pattern of hydrogen donors and acceptors do not correspond. Purines are only complementary with pyrimidines: pyrimidine-pyrimidine pairings are energetically unfavorable because the molecules are too far apart for hydrogen bonding to be established purine-purine pairings are energetically unfavorable because the molecules are too close, leading to electrostatic repulsion. The larger nucleic acids, adenine and guanine, are members of a class of doubly-ringed chemical structures called purines the smaller nucleic acids, cytosine and thymine (and uracil), are members of a class of singly-ringed chemical structures called pyrimidines. The GC base pair has three hydrogen bonds, whereas the AT base pair has only two as a consequence, the GC pair is more stable.
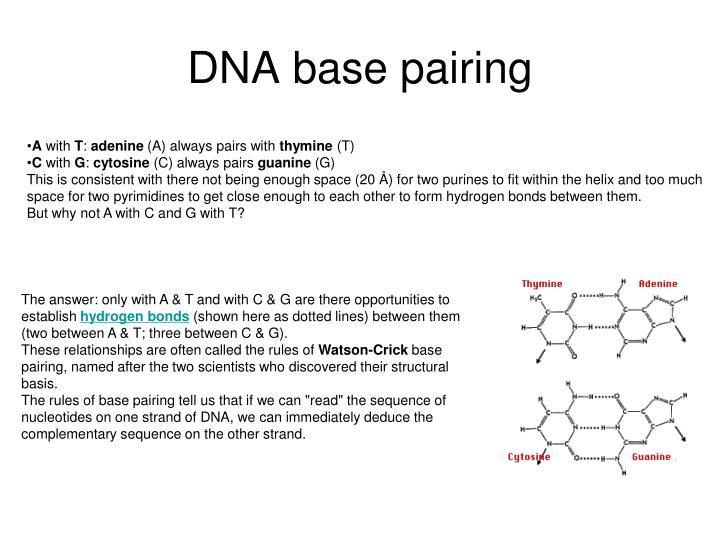
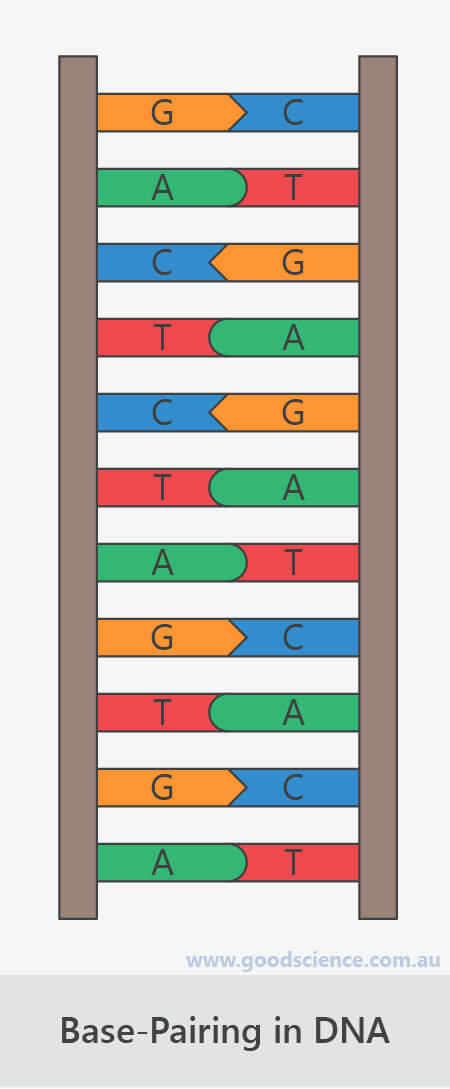
Appropriate geometrical correspondence of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors allows only the "right" pairs to form stably. Hydrogen bonding is the chemical mechanism that underlies the base-pairing rules described above. In case of single stranded DNA/RNA we talk about nucleotides, abbreviated nt (or knt, Mnt, Gnt), rather than base pairs, as they are not paired.įor distinction between units of computer storage and bases kbp, Mbp, Gbp etc may be used for disambiguation. kb (= kbp) = kilo base pairs = 1,000 bp.The following abbreviations are commonly used to describe the length of a DNA/RNA molecule: The corresponding base-paired RNA sequence, in which uracil is substituted for thymine: By convention, the top strand is written from the 5' end to the 3' end thus the bottom strand is written 3' to 5'. The following DNA sequences illustrate pair double-stranded patterns. The haploid human genome (23 chromosomes) is estimated to be about 3 billion base pairs long and to contain 20,000-25,000 distinct genes. Hence, the number of total base pairs is equal to the number of nucleotides in one of the strands (with the exception of non-coding single-stranded regions of telomeres. The size of an individual gene or an organism's entire genome is often measured in base pairs because DNA is usually double-stranded. Some DNA- or RNA-binding enzymes can recognize specific base pairing patterns that identify particular regulatory regions of genes. Non-Watson-Crick base pairing with alternate hydrogen bonding patterns also occur, especially in RNA common such patterns are Hoogsteen base pairs.īase pairing is also the mechanism by which codons on messenger RNA molecules are recognized by anticodons on transfer RNA during protein translation. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil (U). In the canonical Watson-Crick base pairing, adenine (A) forms a base pair with thymine (T), as does guanine (G) with cytosine (C) in DNA. In molecular biology, two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds are called a base pair (often abbreviated bp).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
